Automatic detection of artifacts in converted S3D videos
- Author: Alexander Bokov
- Supervisor: Dmitriy Vatolin
Introduction
Our set of algorithms provides an objective quality assessment for stereoscopic videos converted from a 2D source. In particular, the algorithms are able to detect three types of unwanted effects: edge sharpness mismatch, cardboard effect, and crosstalk noticeability.
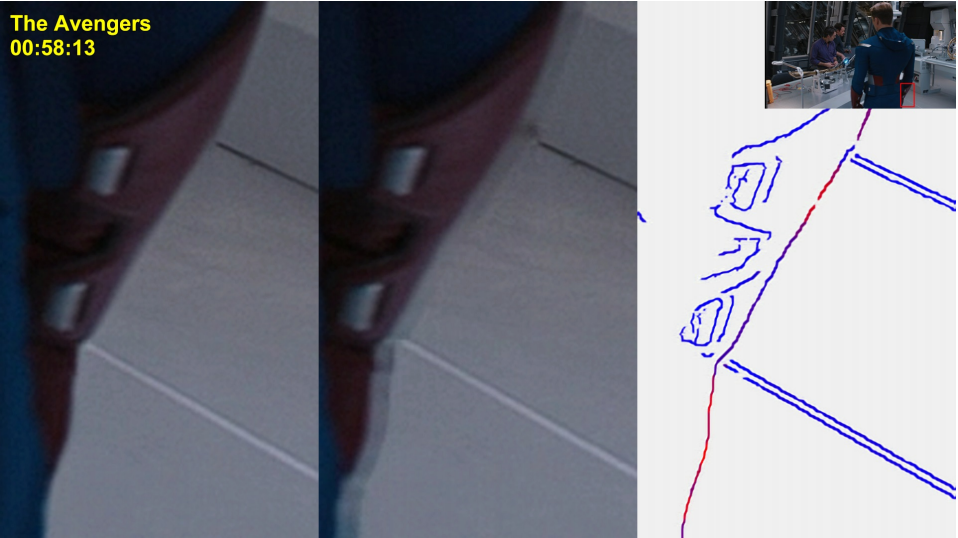
Edge sharpness mismatch
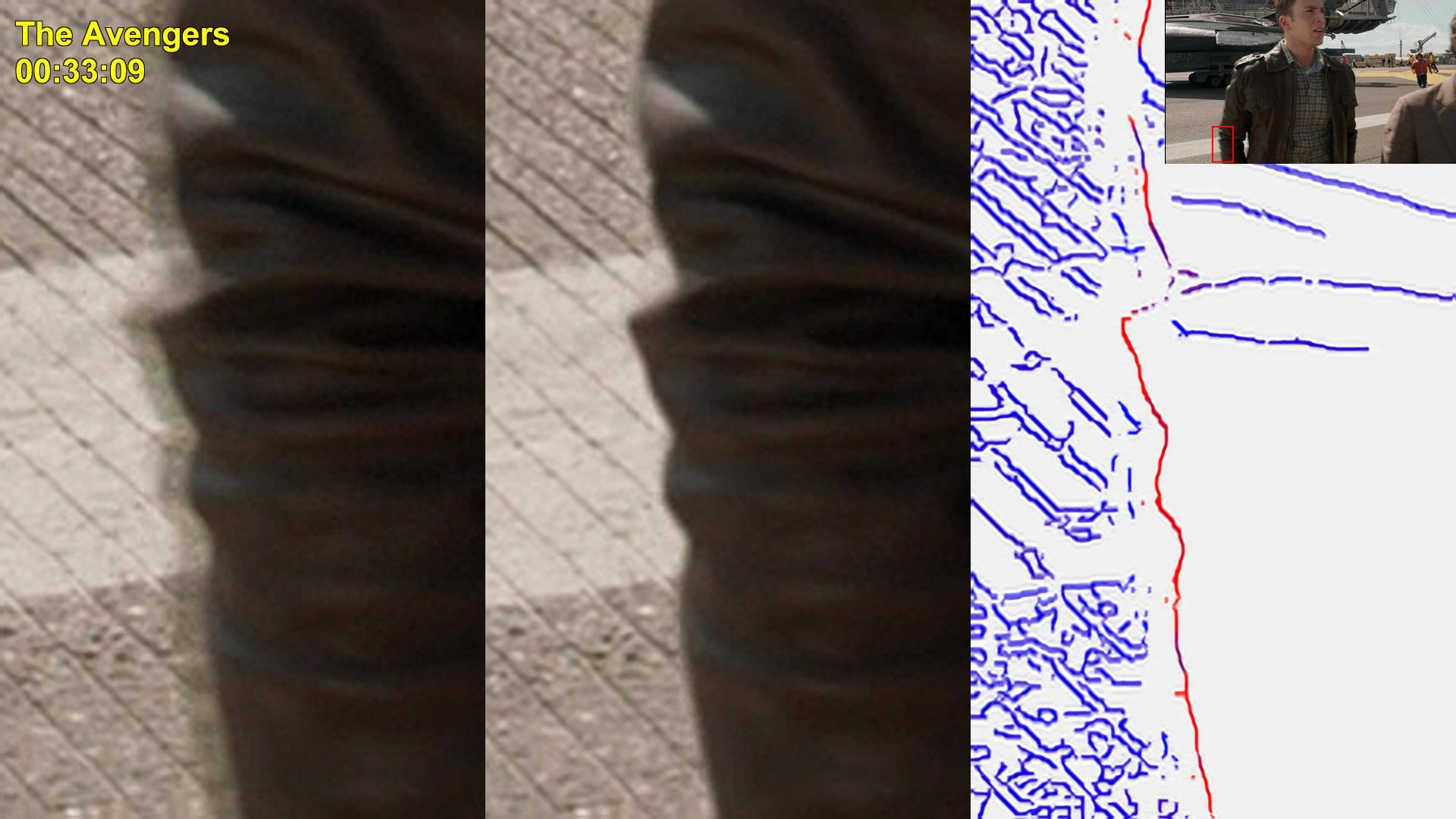

Due to the nature of 2D-to-3D conversion, the sharpness of edges may differ between the left-eye and right-eye views. This artifact is typically caused by the following:
- Use of a “rubber sheet” technique, which involves warping the pixels surrounding the occlusion regions to avoid explicit occlusion filling. In such cases, the edges of the displacement map are blurred and the transition between foreground and background regions is smoothed
- Lack of proper treatment of semi-transparent edges
- Simple occlusion-filling techniques leading to stretching artifacts near object edges
Such an effect is rarely natural. Therefore, the edge sharpness mismatch may cause difficulties with scene interpretation and discomfort for the viewer.
Cardboard effect
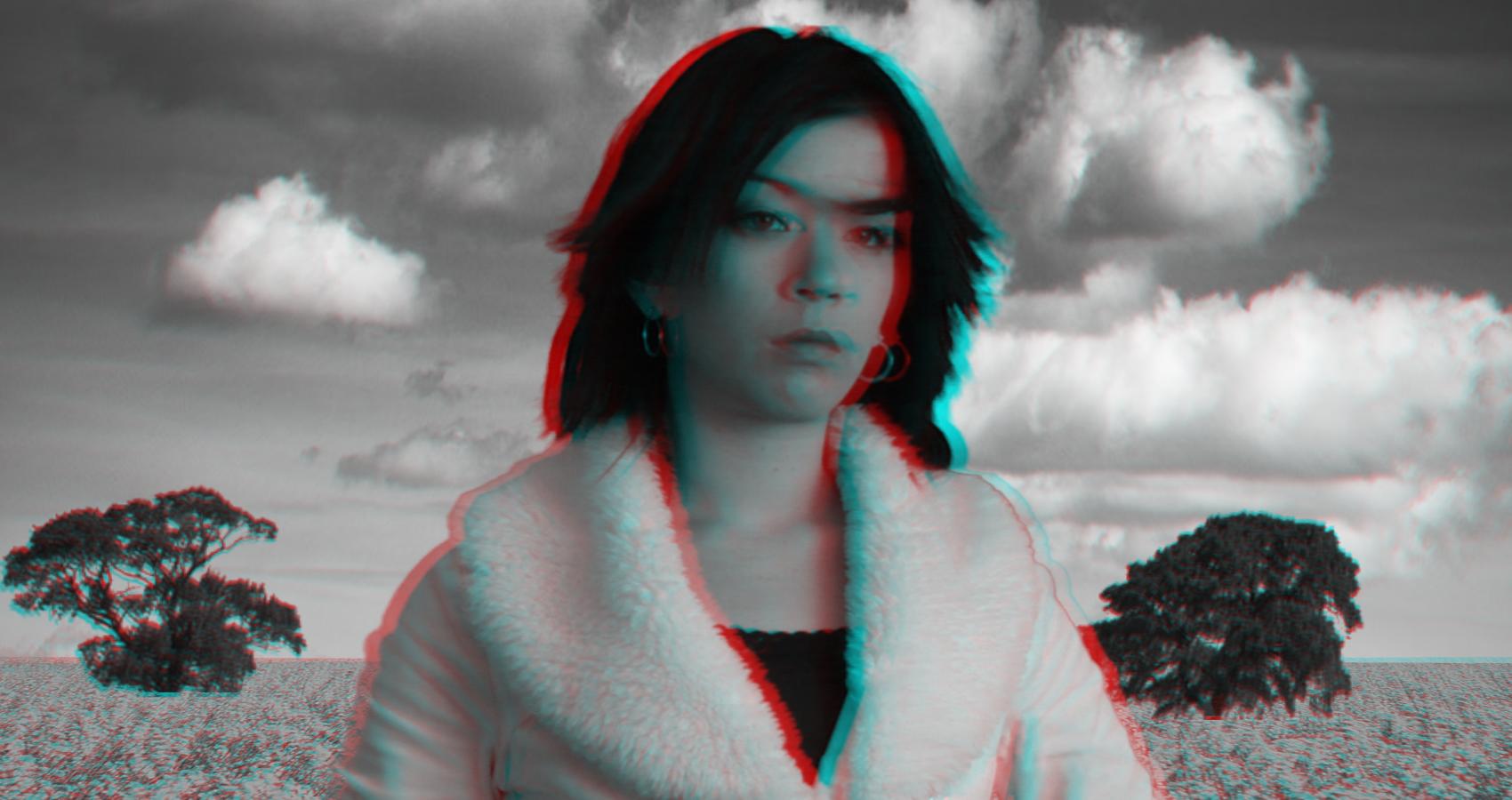
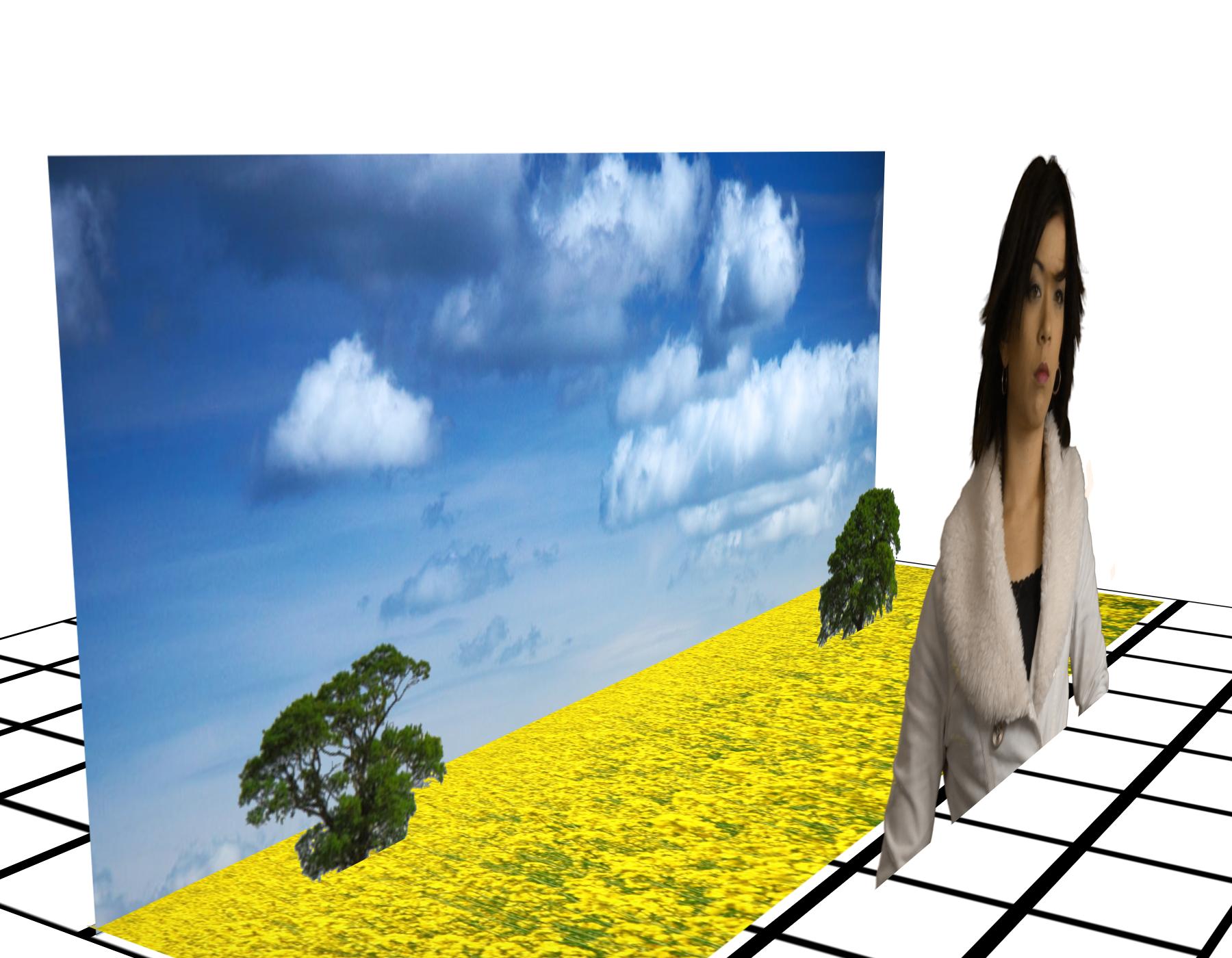


The cardboard effect is a term referring to an unnatural flattening of objects in perceived visual images. Although this artifact may appear in stereoscopic videos captured by a stereoscopic camera system, it appears more frequently in converted S3D videos.
Crosstalk
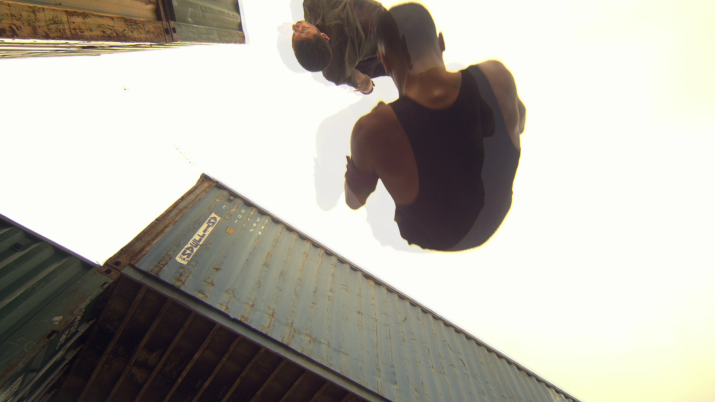

Crosstalk is a very common problem across modern stereo display devices. Both viewer’s eyes see a combination of left and right views. This effect is caused solely by display devices, but it is possible to reduce its noticeability during film production.
Crosstalk visibility depends on the technology used for views separation:
- For 3D glasses with linear polarization the effect visibility increases when the viewer tilts his head from the vertical position.
- 3D glasses with circular polarization aren’t affected by crosstalk.
- Autostereoscopic displays are based on showing different images depending on the viewing angle. Thus the whole viewing angle is divided into several zones. The effect takes place if the viewer is between these zones.
- The VR headset is one of the few 3D display technologies that are fully unaffected by crosstalk. Such quality is accomplished by using separate displays for each eye.
Proposed method
For each type of the artifacts we have developed a detection algorithm.
Edge sharpness mismatch algorithm
This complex task can be simplified assuming that background remains the same near edges with sharpness mismatch.
- Detect edges using Canny algorithm and match them across views via block disparity estimation method;
- Analyze the edges, create a preliminary sharpness mismatch map;
- Estimate a map of background changes;
- Refine the preliminary mismatch map using the estimate of background changes.
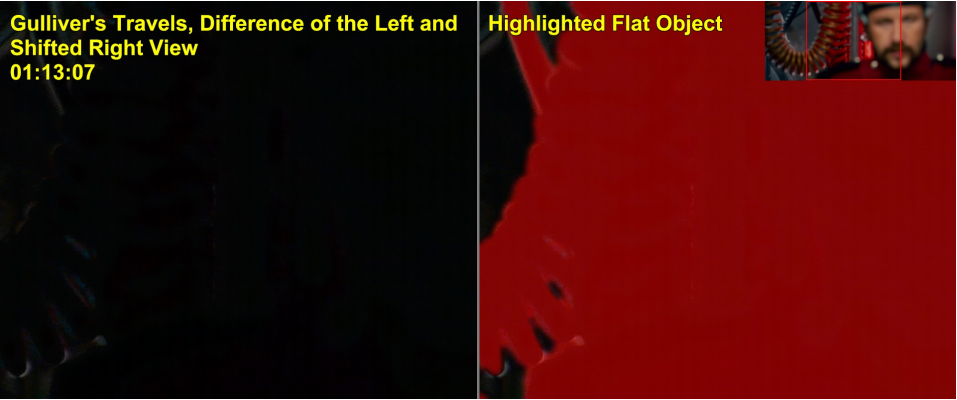
Cardboard effect
In a 2D video the true depth map is not available and the converted video’s disparity cannot be verified. Thus, our goal is to detect completely flat objects and scenes.
- Calculate the disparity map;
- Disparity map segmentation;
- For each object, estimate its flatness using the difference between left view and warped image of right view;
- Choose the most flat object and output its measure of flatness.
Flat scenes are detected in the same way. Scenes that were rotated (with disparity changing linearly) are also considered flat.
Crosstalk noticeability
In highly textured regions the crosstalk can be masked by the human visual system. That is why we use a structural similarity function to compute the noticeability of differences. We blend the left and right views in 85% to 15% proportion.
- Construct a Gaussian pyramid for the left view and the blended view;
- Compute gradient maps for the views on each pyramid level;
- Compute the texture similarity map;
- Combine the gradient and similarity maps into the resulting noticeability map.
Experiments
The following images demonstrate the work of our algorithm. The regions with distortions are enlarged, and a thumbnail of the full view is placed in the corner.




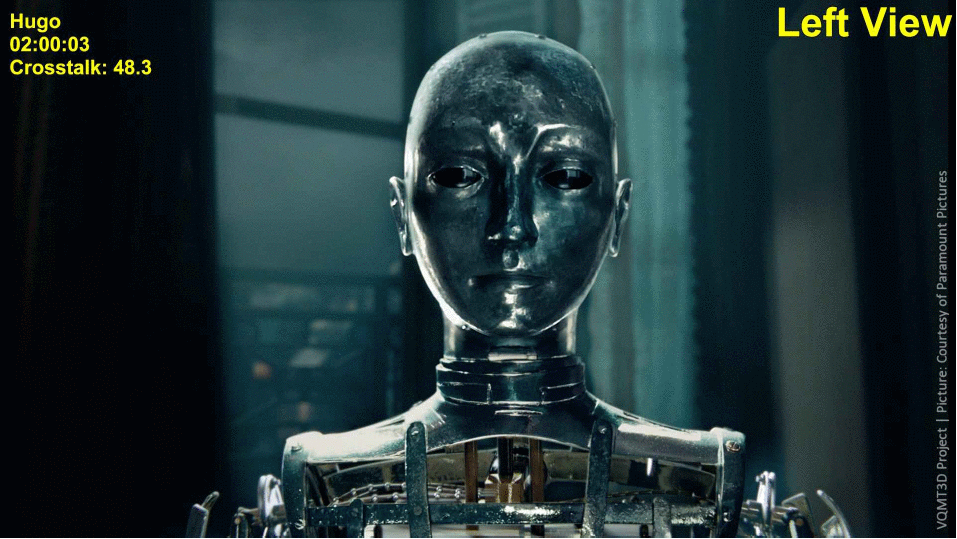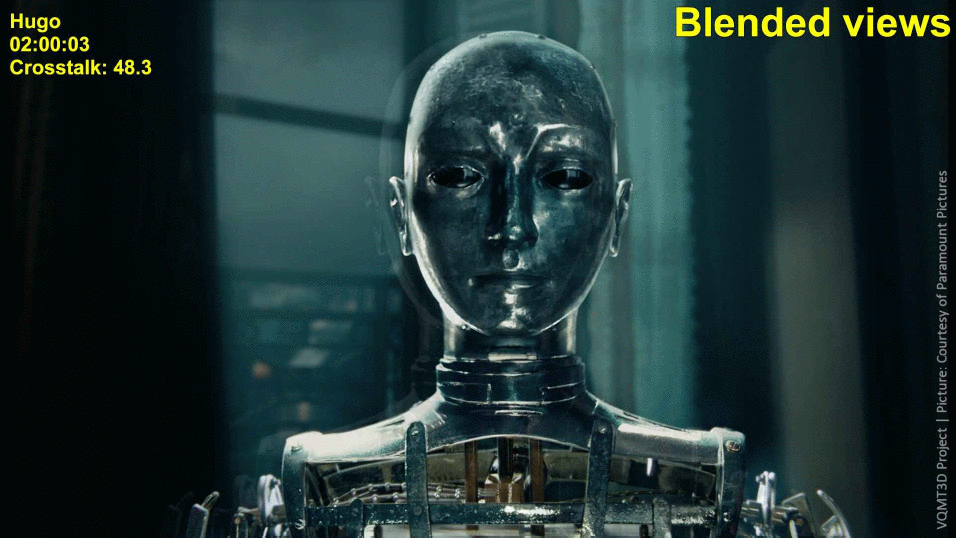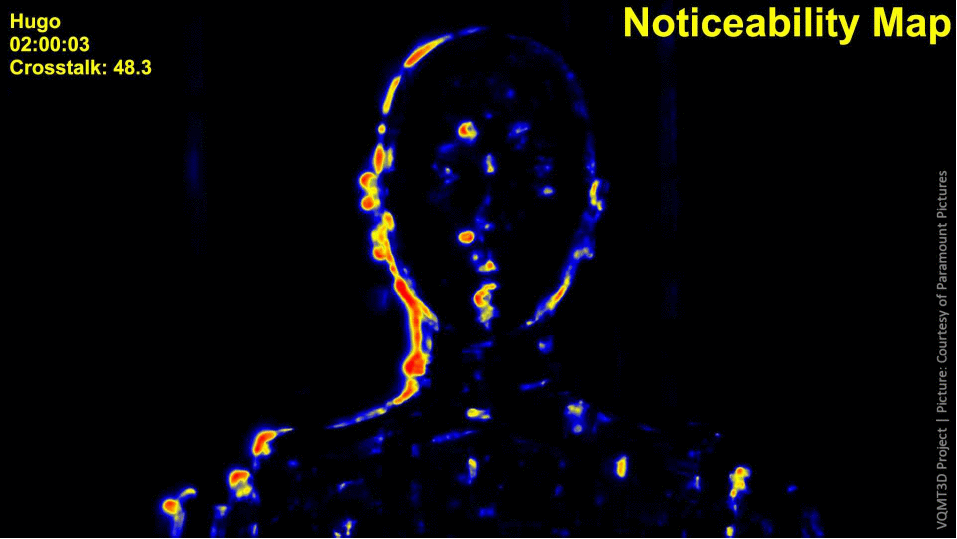
Results
- Our method detects scenes from the input video with the largest edge sharpness mismatch, cardboard effect and crosstalk noticeability.
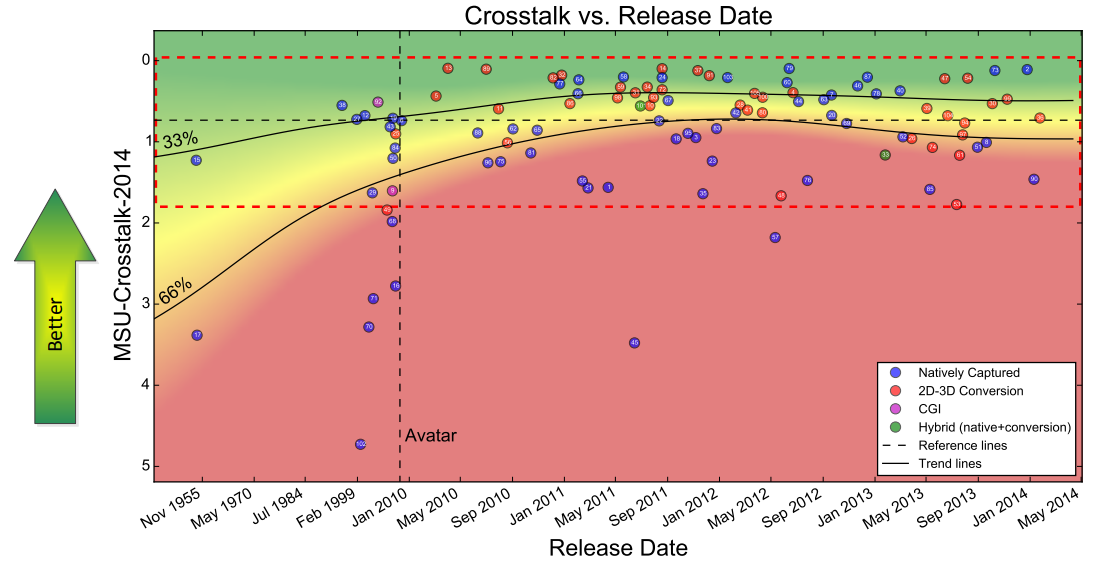
- Though metrics calculate an approximate estimate and the final decision is up to a human expert, it comes with very high precision. Based on our experiments, the edge sharpness mismatch metric has 84% precision.
- On an Intel Core i7-3632QM our crosstalk noticeability algorithm runs at 0.21s per stereo pair at 960x540 resolution.
Publications
A. Bokov et al., "Automatic detection of artifacts in converted S3D video," in Stereoscopic Displays and Applications XXV, Vol. 9011, 2014.
-
MSU Benchmark Collection
- Super-Resolution Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Super-Resolution Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Video Colorization Benchmark
- Video Saliency Prediction Benchmark
- LEHA-CVQAD Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Learning-Based Image Compression Benchmark
- Super-Resolution for Video Compression Benchmark
- Defenses for Image Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Deinterlacer Benchmark
- Metrics Robustness Benchmark
- Video Upscalers Benchmark
- Video Deblurring Benchmark
- Video Frame Interpolation Benchmark
- HDR Video Reconstruction Benchmark
- No-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Full-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Video Alignment and Retrieval Benchmark
- Mobile Video Codecs Benchmark
- Video Super-Resolution Benchmark
- Shot Boundary Detection Benchmark
- The VideoMatting Project
- Video Completion
- Codecs Comparisons & Optimization
- VQMT
- MSU Datasets Collection
- Metrics Research
- Video Quality Measurement Tool 3D
- Video Filters
- Other Projects
