Detection of object boundary inconsistencies between 2D-3D conversion results and depth maps
- Author: Stanislav Dolganov
- Supervisor: dr. Dmitriy Vatolin
Introduction
The creation of S3D movies by converting 2D captured footage requires the high-quality depth maps. In case of inaccurate depth maps’ usage during the conversion different types of artifacts can occur. Such artifacts can make the viewing experience significantly worse even if it appears only in the background.
Our method extracts information about motion in the scene and detects conversion-related discrepancies between motion strength and depth.
An example of a scene containing a defect found by the proposed method: the foreground object was merged with the background.

Proposed method
Algorithm scheme
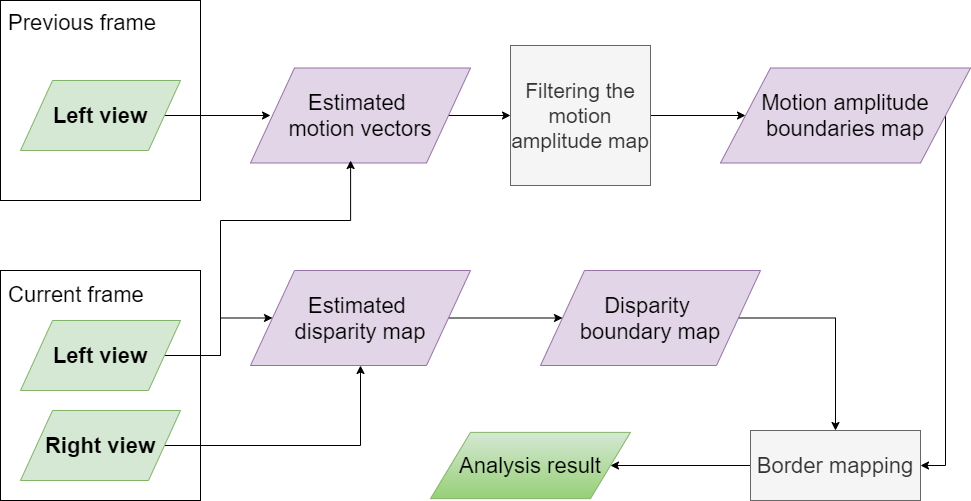
The disparity map estimation step may be skipped if the original depth map is available.
Experiments
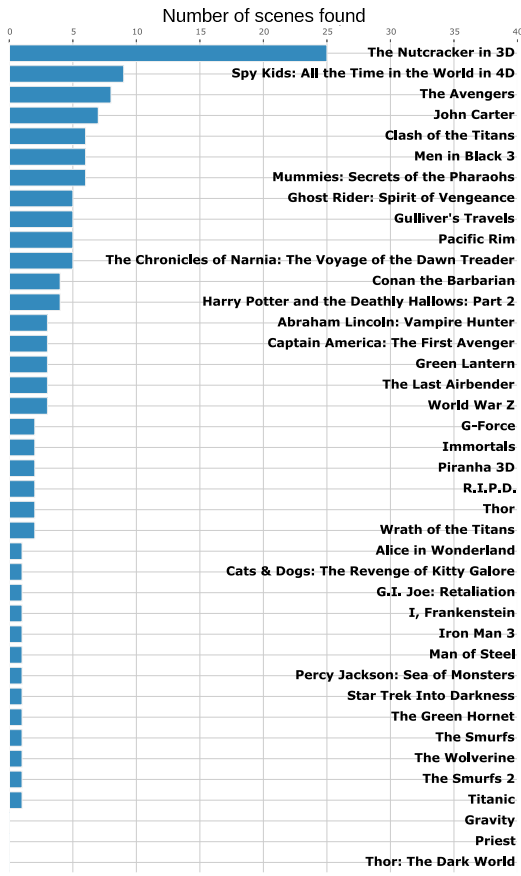
The algorithm was tested on 39 converted stereoscopic feature movies. As a result, 125 scenes with this artifact were found.
The number of scenes with notable artifacts found during the analysis of feature movies are illustrated below.
The examples of detected scenes are listed below. In these scenes, foreground objects merge with the background.
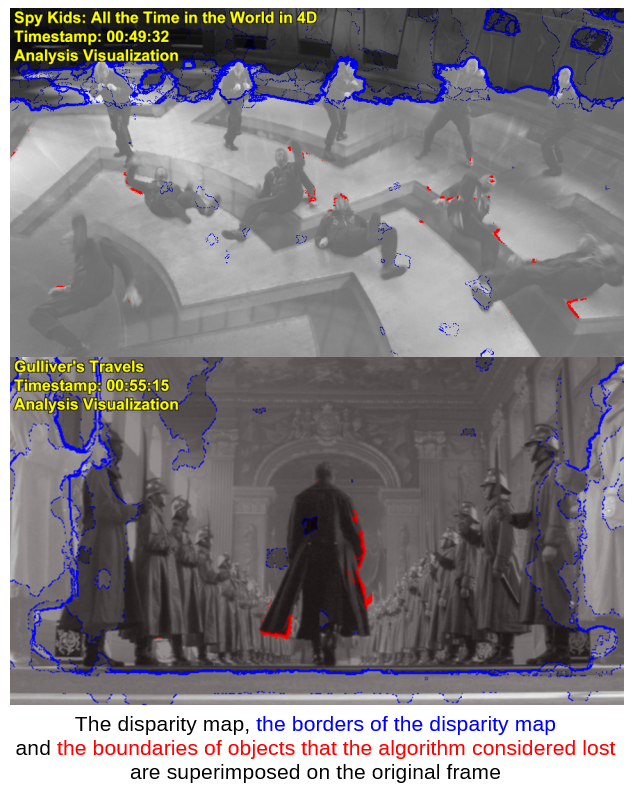

-
MSU Benchmark Collection
- Video Colorization Benchmark
- Video Saliency Prediction Benchmark
- LEHA-CVQAD Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Learning-Based Image Compression Benchmark
- Super-Resolution for Video Compression Benchmark
- Defenses for Image Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Super-Resolution Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Deinterlacer Benchmark
- Metrics Robustness Benchmark
- Video Upscalers Benchmark
- Video Deblurring Benchmark
- Video Frame Interpolation Benchmark
- HDR Video Reconstruction Benchmark
- No-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Full-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Video Alignment and Retrieval Benchmark
- Mobile Video Codecs Benchmark
- Video Super-Resolution Benchmark
- Shot Boundary Detection Benchmark
- The VideoMatting Project
- Video Completion
- Codecs Comparisons & Optimization
- VQMT
- MSU Datasets Collection
- Metrics Research
- Video Quality Measurement Tool 3D
- Video Filters
- Other Projects
