Detection of 3D movie scenes shot on converged axes
- Author: Kirill Malyshev
- Supervisor: dr. Dmitriy Vatolin
Introduction
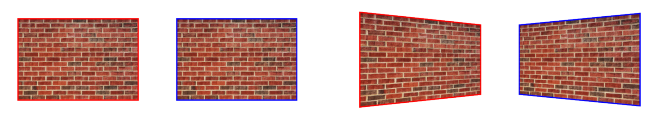
During the shooting of a close-up with a stereo rig, where the distance between camera axes is bigger than the gap between the visual axes of the eyes, novice operators often have to set up the cameras to make the optical axes concurrent. In other words, they have to shoot on converged axes instead of parallel ones. This method can still be used, but it requires a lot of (competent) effort. The discussion of the details goes beyond the scope of this article, so let’s just mention that shooting of close-ups on converged axes causes the vertical parallax and rather unpleasant distortions of the objects’ shapes in the image:

Shooting of close-ups on converged axes causes the vertical parallax and distortions of the objects’ shapes in the image. At the same time, the picture, normally perceived in real life (since the brain is able to fix such distortions), will look uncomfortable in the movies. This effect can be significantly reduced, but you have to get the idea of particular scene geometry and the range of problems that you are going to face after shooting. Content shot on parallel axes also has to be checked during the post-reduction stage, but this is more simple than shooting on converged axes.
Keystone distortion is caused in the stereoscopic video when the optical axes of the cameras are not parallel during shooting. When comparing left and right views of a stereoscopic image captured this way, you can notice a distinctive feature of keystone distortion — when moving from the left view to the right, the left side of the image is compressed to the center, and the right side of the image expands from the center.

Proposed method
A neural network approach is used to detect converged axes.
Dataset generation
A synthetic dataset was created using GTA V computer game to train the model. A mod was written that allows to automate the movement of a playable character and capture stereoscopic frames at a given frequency. To get various data, camera convergence angle, the direction of the camera, the weather and the time of day were chosen randomly for each frame.

For more realistic views, most of the frames were modified with noise and/or blur.

Model architecture
The architecture of the model is a convolutional neural network. The input receives calculated disparity map for left view and confidence map for it. The model returns one number — the value of the angle between converged optical axes in degrees. As a loss function, MSE was used.

Experiments
A total of 12 full-length stereoscopic movies were tested:
- Avatar 3D (2009)
- Cirque du Soleil: Worlds Away (2012)
- The Darkest Hour (2011)
- Dolphin Tale (2011)
- Flying Swords of Dragon Gate (2011)
- Drive Angry (2011)
- The Final Destination (2009)
- The Three Musketeers (2011)
- Step Up 3D (2010)
- A Very Harold & Kumar 3D Christmas (2011)
- 3D Sex & Zen: Extreme Ecstasy (2011)
- Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides (2011)
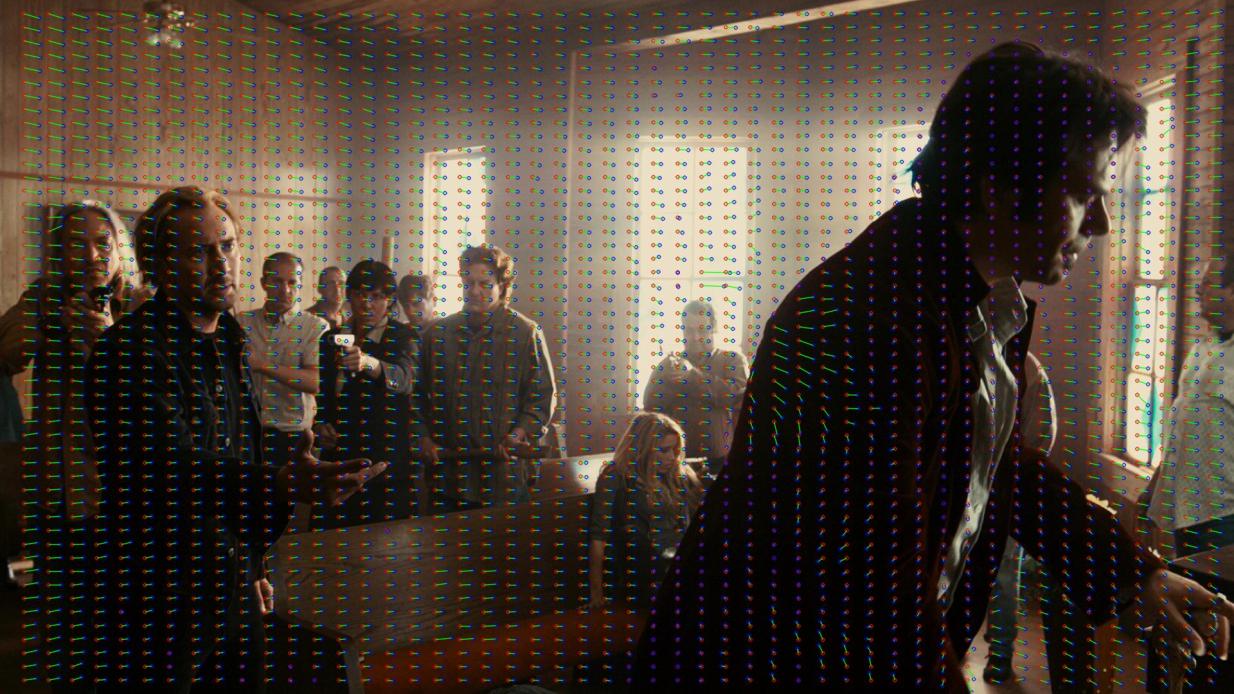
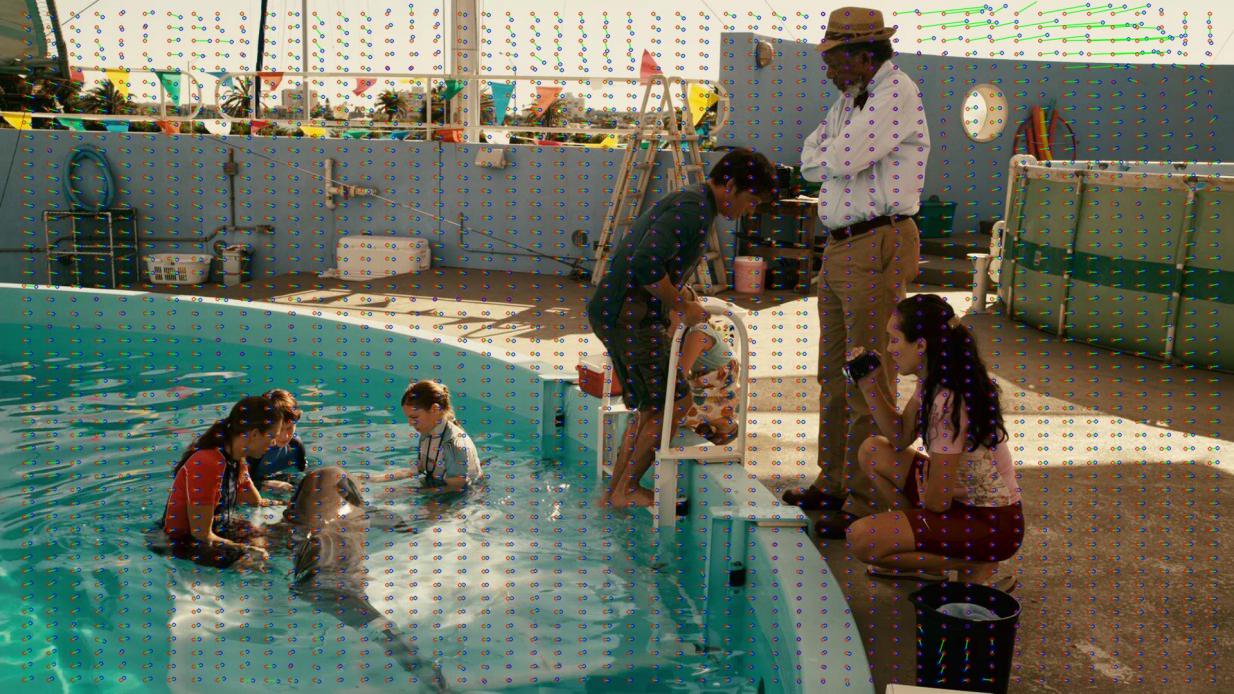
In the examples below, you can see visualizations of disparity maps with keystone distortions. Red indicates the disparity vectors in the left view, blue — in the right one.
Step Up 3D
Drive Angry

Avatar 3D
![]()
Dolphin Tale

Results
- 54 distorted scenes were found in Drive Angry and 23 in Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides. For all tested movies, the AUC reaches 0.937.
- The average speed of the model on the GeForce GTX 1050 Ti is 20 frames per second.
-
MSU Benchmark Collection
- Super-Resolution Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Super-Resolution Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Video Colorization Benchmark
- Video Saliency Prediction Benchmark
- LEHA-CVQAD Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Learning-Based Image Compression Benchmark
- Super-Resolution for Video Compression Benchmark
- Defenses for Image Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Deinterlacer Benchmark
- Metrics Robustness Benchmark
- Video Upscalers Benchmark
- Video Deblurring Benchmark
- Video Frame Interpolation Benchmark
- HDR Video Reconstruction Benchmark
- No-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Full-Reference Video Quality Metrics Benchmark
- Video Alignment and Retrieval Benchmark
- Mobile Video Codecs Benchmark
- Video Super-Resolution Benchmark
- Shot Boundary Detection Benchmark
- The VideoMatting Project
- Video Completion
- Codecs Comparisons & Optimization
- VQMT
- MSU Datasets Collection
- Metrics Research
- Video Quality Measurement Tool 3D
- Video Filters
- Other Projects
